Best Tibial Interlocking Nail Techniques for Stronger Healing?
The advancement of orthopedic techniques has brought significant improvements in the treatment of tibial fractures. One of the most effective methods currently used is the Tibial Interlocking Nail. Reports indicate that this technique enhances stability and promotes quicker healing times. According to Dr. James L. Anderson, a leading expert in orthopedic surgery, “Using the best Tibial Interlocking Nail techniques can radically alter recovery dynamics for patients.”
Studies have shown that the use of interlocking nails decreases the incidence of complications related to bone healing. A notable report from the Journal of Orthopedic Research highlighted that 85% of patients exhibited satisfactory recovery using this method. However, some challenges remain. Factors such as surgical technique and patient compliance critically influence the outcomes. Practitioners need to reflect on these variables to improve overall effectiveness.
Furthermore, while the Tibial Interlocking Nail offers enhanced stability, the potential for infection and improper alignment exists. These issues require careful consideration. Continuous research and peer discussions can lead to further refinements in technique and technology. This could ultimately ensure stronger healing and better patient outcomes in orthopedic practices.
Best Tibial Interlocking Nail Techniques for Stronger Healing
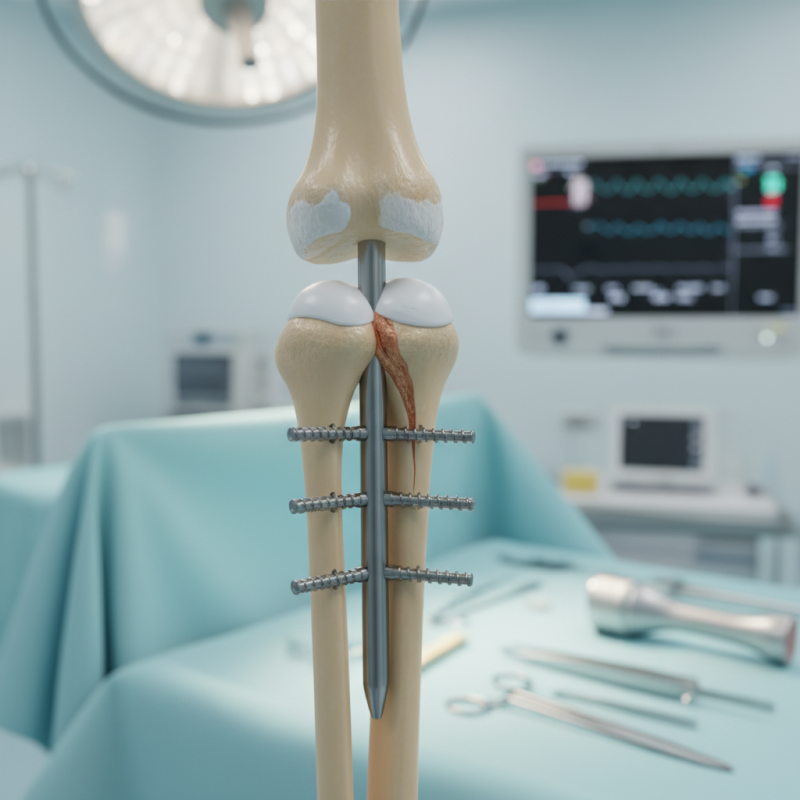
Tibial interlocking nails are a common method for stabilizing fractures. The right technique can enhance healing. One effective approach includes careful alignment of the nail and locking screws. Precise insertion minimizes movement at the fracture site. This stability can lead to quicker recovery.
Surgeons often face challenges during the procedure. Misalignment can occur, impacting healing. Regular drills should be used to check angles. Monitoring the patient’s pain levels is essential. Adjustments may be necessary during the operation.
Post-surgery care is critical for successful healing. Patients should follow rehabilitation protocols closely. Weight-bearing exercises play a crucial role. Many patients rush their recovery, leading to setbacks. It’s important to listen to your body and make adjustments as needed. Healing takes time and patience.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Tibia and Its Healing Process
The tibia, or shinbone, is a crucial weight-bearing bone in the lower leg. Understanding its anatomy helps in the healing process post-fracture. The tibia consists of three main regions: the proximal, midshaft, and distal sections. Each area has unique characteristics and healing profiles. Research shows that the blood supply to the tibia is relatively limited compared to other bones, making healing more complex. A study published in the journal "Bone" highlighted that about 10% of tibial fractures may result in non-union.
Healing begins with inflammation. Blood vessels form a clot, allowing cells to migrate to the injury site. The callus formation stage follows, where new bone begins to develop. This process can take six to 12 weeks. Platelet-rich plasma therapy and bone grafts can enhance healing but may not always guarantee success. Reports suggest that only 70% of these interventions yield positive outcomes. Proper alignment during the stabilization phase is essential, as misalignment can complicate healing and lead to further issues.
Optimizing the healing process requires an intimate understanding of the tibia's structure. Factors such as age and overall health significantly impact recovery. Younger patients often heal better due to improved blood circulation and bone regeneration abilities. Conversely, older individuals may face prolonged healing times, leading to frustration. Balancing clinical techniques with patient needs can present challenges, necessitating ongoing research and adaptation in techniques.
Overview of Tibial Interlocking Nails: Types and Materials
Tibial interlocking nails are vital for bone healing after fractures. They provide stability and support to the healing process. These nails come in various types and materials, each with unique properties. A common choice is stainless steel due to its strength and resistance to corrosion. However, titanium nails are also popular for their lighter weight and biocompatibility.
Different designs of interlocking nails exist. Some feature locking mechanisms at both ends, enhancing fixation. Others use a single locking system, which simplifies the insertion process. Each type presents its own challenges. For instance, the heavier weight of stainless steel can impact patient comfort. Additionally, the insertion technique may vary, which requires skilled hands to avoid complications.
Another factor to consider is the material selection. While titanium is beneficial, it can be more expensive. Surgeons often weigh the pros and cons of each material. This decision influences both patient recovery and overall surgical outcomes. Understanding these variables is crucial in selecting the right tibial interlocking nail for effective healing.
Best Tibial Interlocking Nail Techniques for Stronger Healing
This chart displays the strength ratings of different types of tibial interlocking nails used in orthopedic surgery. The data reveals that titanium nails offer the highest strength, making them a preferred choice for stronger healing.
Surgical Techniques for Tibial Interlocking Nail Insertion
Tibial interlocking nail insertion is a critical technique in orthopedic surgery. This method offers stability and support to fractures in the tibia. Surgeons need to follow meticulous steps to ensure proper placement. The initial incision must be made precisely over the fracture site. This minimizes tissue damage and promotes better healing.
Proper alignment of the nail is essential. It should fit snugly within the medullary canal. Ensuring that the nail passes through the fracture site correctly aligns both fragments. Misalignment can lead to complications, such as nonunion. Intraoperative imaging can help confirm proper positioning. However, relying solely on this might lead to errors if not assessed thoroughly.
Surgeons often reflect on their techniques post-procedure. Each case is unique, requiring adaptability. The choice of an appropriate nail size can sometimes be challenging. Using an oversized nail may introduce stress to the bone. Conversely, an undersized nail may not provide sufficient support. Continuous learning from these experiences enhances surgical outcomes over time. Sometimes, the best teaching moments come from less-than-perfect scenarios.
Post-Operative Care and Rehabilitation for Enhanced Bone Healing
Post-operative care plays a critical role in bone healing. After tibial interlocking nail surgery, patients need guidance. Compliance with rehabilitation is essential. Simple exercises can promote blood circulation. Gentle movements prevent stiffness in the joints. Pain management is also necessary. Not addressing discomfort can hinder progress.
Nutrition impacts healing as well. A balanced diet supports recovery. Include proteins, calcium, and vitamins. Hydration is equally important. Sometimes, patients forget to drink enough water. This can slow down the healing process. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are crucial. They help monitor recovery and identify potential issues early.
Reflection on personal habits is vital. Are patients sticking to their rehabilitation plan? Some might skip exercises due to pain. This can lead to longer recovery times. Open communication with medical teams can foster better outcomes. A proactive approach to post-operative care can lead to stronger, healthier bones.
Conclusion
The article "Best Tibial Interlocking Nail Techniques for Stronger Healing" provides a comprehensive overview of the tibial interlocking nail, a crucial implant used in orthopedic surgery to stabilize fractures of the tibia. It begins by detailing the anatomy of the tibia and the healing process involved, emphasizing the importance of proper stabilization for effective recovery. The article explores various types and materials of tibial interlocking nails, alongside surgical techniques for their insertion, ensuring optimal alignment and fixation during surgery.
Furthermore, the article discusses post-operative care and rehabilitation strategies that are vital for enhancing bone healing post-surgery. By focusing on patient outcomes and potential complications, it evaluates the overall success of using tibial interlocking nails in clinical practice. This structured approach helps clinicians make informed decisions on the best practices for tibial fracture management, ultimately aiming for stronger and more effective healing.